

Table of contents
- What is a heat pump?
- How does a heat pump work?
- intuis, as a leader in utilizing the natural R290 refrigerant
- What are the different types of heat pumps?
- What are the advantages of a heat pump?
- What are the disadvantages of a heat pump?
- Is a heat pump economical?
- What is the average cost of a heat pump?

Table of contents
- What is a heat pump?
- How does a heat pump work?
- intuis, as a leader in utilizing the natural R290 refrigerant
- What are the different types of heat pumps?
- What are the advantages of a heat pump?
- What are the disadvantages of a heat pump?
- Is a heat pump economical?
- What is the average cost of a heat pump?

What is a heat pump?
A heat pump, also known as a HPAC (Heat Pump and Air Conditioning) or PAC (Pompe à Chaleur in French), is a device that extracts heat from the air (air source) or the ground (ground source) and transfers it to a building, a water-based heating system, or a ventilation system. Some heat pumps are reversible, meaning they can provide both heating and cooling to a space. It's an environmentally friendly process that utilizes readily available, free, and renewable heat to meet our energy needs.
How Does a Heat Pump Work?
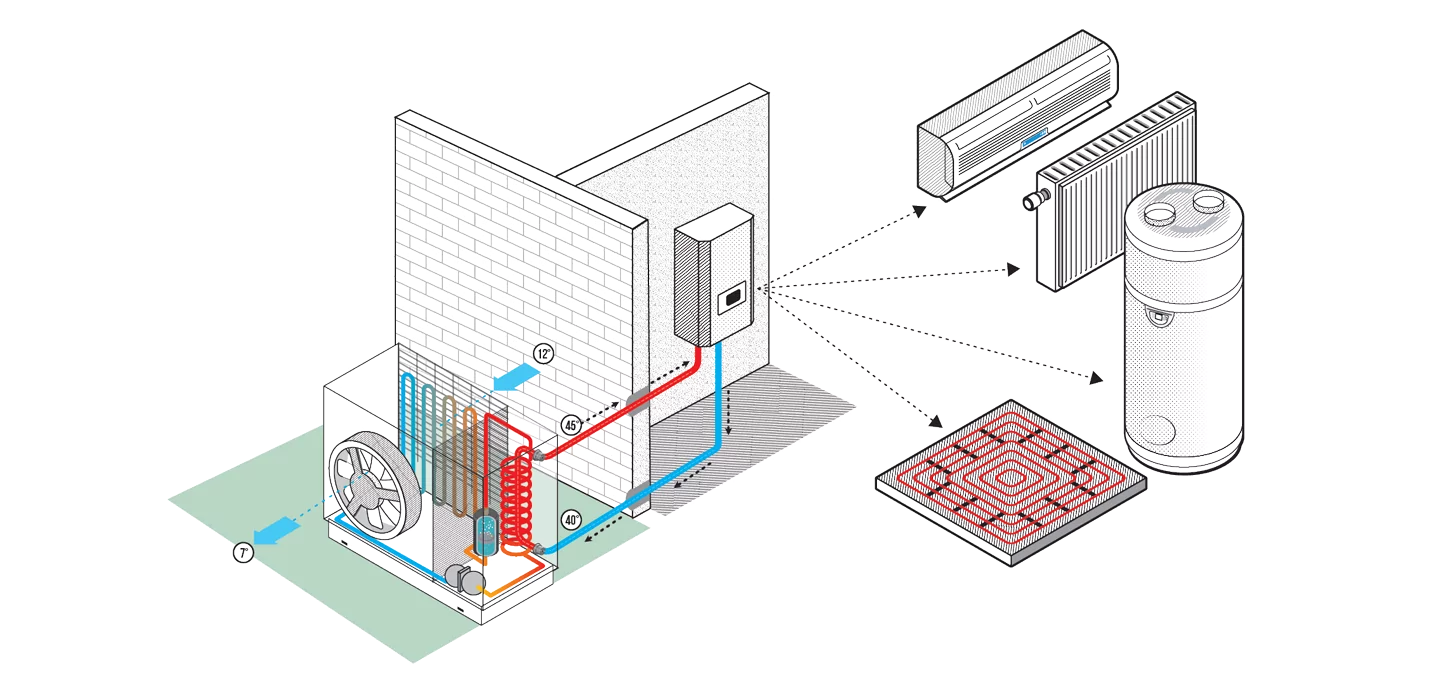
A heat pump captures energy from an external source (air, water, or ground) using an evaporator, then raises the temperature of this thermal energy through a compressor, and finally transfers it, at the desired temperature, to the space that needs heating or cooling.
A heat pump operates similarly to a refrigerator and comprises four main components:
- Evaporator: This component transfers the heat extracted from the environment to the refrigerant fluid. To do this, the refrigerant must be colder than the external air. The expelled air is typically about 5°C cooler. It uses the evaporator's fins to allow heat to warm the fluid inside the heat pump's circuit, causing its evaporation.
- Compressor: The gaseous refrigerant is compressed to increase both pressure and temperature significantly. This is achieved through a compressor, which operates like a bicycle pump, heating the working fluid considerably as it transitions from low-pressure gas to high-pressure gas.
- Condenser: The condenser transfers the heat contained in the refrigerant to the hydraulic circuit. As a result, the refrigerant condenses, changing from a gaseous to a liquid state. The hydraulic connection benefits from this change in state by absorbing heat (about +5°C). It then travels from the heat pump to the indoor unit to heat the heating and domestic hot water circuit.
- Expansion Valve: The refrigerant's pressure is lowered, and it is significantly cooled down through an expansion valve (adiabatic expansion). The purpose is to recharge it with heat for the next cycle. The loop is complete.
The choice of refrigerant fluid is crucial in the process. In recent years, there has been a shift towards using R32 refrigerant, which is 70% less harmful to the environment. However, this gas remains quite polluting and is prohibited by the F-GAS regulation, which advocates for more natural fluids like R290 (propane). These alternatives do not contain HFCs (hydrofluorocarbons) and are 325 times less harmful to the environment. The degree of harm is measured by the Global Warming Potential (GWP), which is 3 for R290 and 675 for R32.
That's why Intuis made the forward-looking choice in 2010 to use R290 for its equipment.
intuis, as a leader in utilizing the natural R290 refrigerant, offers exceptional thermal performance while adhering to environmental standards.
intuis s'est démarqué en adoptant dès 2010 le fluide R290, également connu sous le nom de propane, pour ses équipements. Contrairement au R32, le R290 respecte la norme européenne F-GAS en atteignant un indice de seulement 150, soit une réduction de 80%.
Le choix précurseur et visionnaire d'Intuis il y a 13 ans repose sur les avantages environnementaux du R290, un fluide naturel dont l'empreinte carbone est évaluée à 3. En plus de son impact positif sur l'environnement, le R290 offre des performances thermiques exceptionnelles.
Aujourd'hui, plus de la moitié des acteurs du marché rejoignent Intuis dans cette tendance, afin de se conformer aux exigences légales et environnementales. Fort de son savoir-faire et de son expérience, Intuis est devenu un expert et une référence incontournable dans ce domaine.
What are the different types of heat pumps?
Within the field of aerothermal heat pumps, we can distinguish between air-to-water heat pumps and air-to-air heat pumps:
- Air-to-Water Heat Pumps: hese systems extract heat from the outdoor air and use a fluid to transfer it to the water in the building's heating network. This heats up the central heating system (water radiators or underfloor heating) and domestic hot water. Air-to-water heat pumps provide heating, cooling, and domestic hot water using emitters placed on the ceiling or in the floor and radiators. They operate silently through radiant heating, without forced air. These are used in new constructions or renovations if a hydraulic circuit already exists.
- Air-to-Air Heat Pumps: These devices extract heat from the outdoor air and transfer it, via a fluid, to the indoor air of the building. They can provide both heating and air conditioning.
What are the advantages of a heat pump?
- A heat pump allows for energy savings because it utilizes a free and renewable energy source: outdoor air. Its performance and cost savings are linked to the ratio of energy absorbed to energy produced.
- A heat pump does not rely on fossil fuels for operation.
- It does not emit any odors during operation.
- It offers the possibility of cooling indoor air.
- Some models are compatible with solar solutions (thermal and photovoltaic), and hybrid systems are available.
What are the disadvantages of a heat pump?
- Installing a heat pump requires maintaining a minimum clearance space of 2 meters around the unit and a distance of 30 to 50 cm from the wall, depending on the model. This facilitates air circulation and the heat pump's performance.
- Under no circumstances should it be placed in an enclosed space without adequate ventilation that ensures 80% of the heat pump's ventilation flow.
Is a heat pump economical?
A heat pump is very economical in the medium term. It is estimated that homeowners can achieve savings of up to 75% compared to traditional heating sources. However, a heat pump's consumption depends on its power, the size of the property, ceiling height, insulation quality, and the region's climate.
Proper sizing is crucial, as an undersized heat pump will overconsume for inadequate comfort, requiring supplementary heating.
Beware of false economies: opting for a less powerful system may not deliver the expected results. There are hybrid solutions available if you wish to retain existing systems.

What is the average cost of a heat pump?
The cost of an air-source heat pump (excluding installation) ranges from €3,000 to €13,000, depending on the model and type of heat pump (air-to-air or air-to-water). While the initial investment is high, it can result in annual energy bill savings of up to €1,000. The installation costs can be offset by government financial incentives.
source : hellowatt.fr


