
Table of contents

Table of contents
Are you in search of an efficient and environmentally friendly heating system? The heat pump is an option to consider. Economical in operation, its principle is simple: it extracts heat from the air, water, or ground and transfers it into a building. However, there are various types of heat pumps, such as hydrothermal heat pumps, geothermal heat pumps, and aerothermal heat pumps. Each comes with its unique features and advantages. Let's take a closer look.
What Is a Heat Pump?
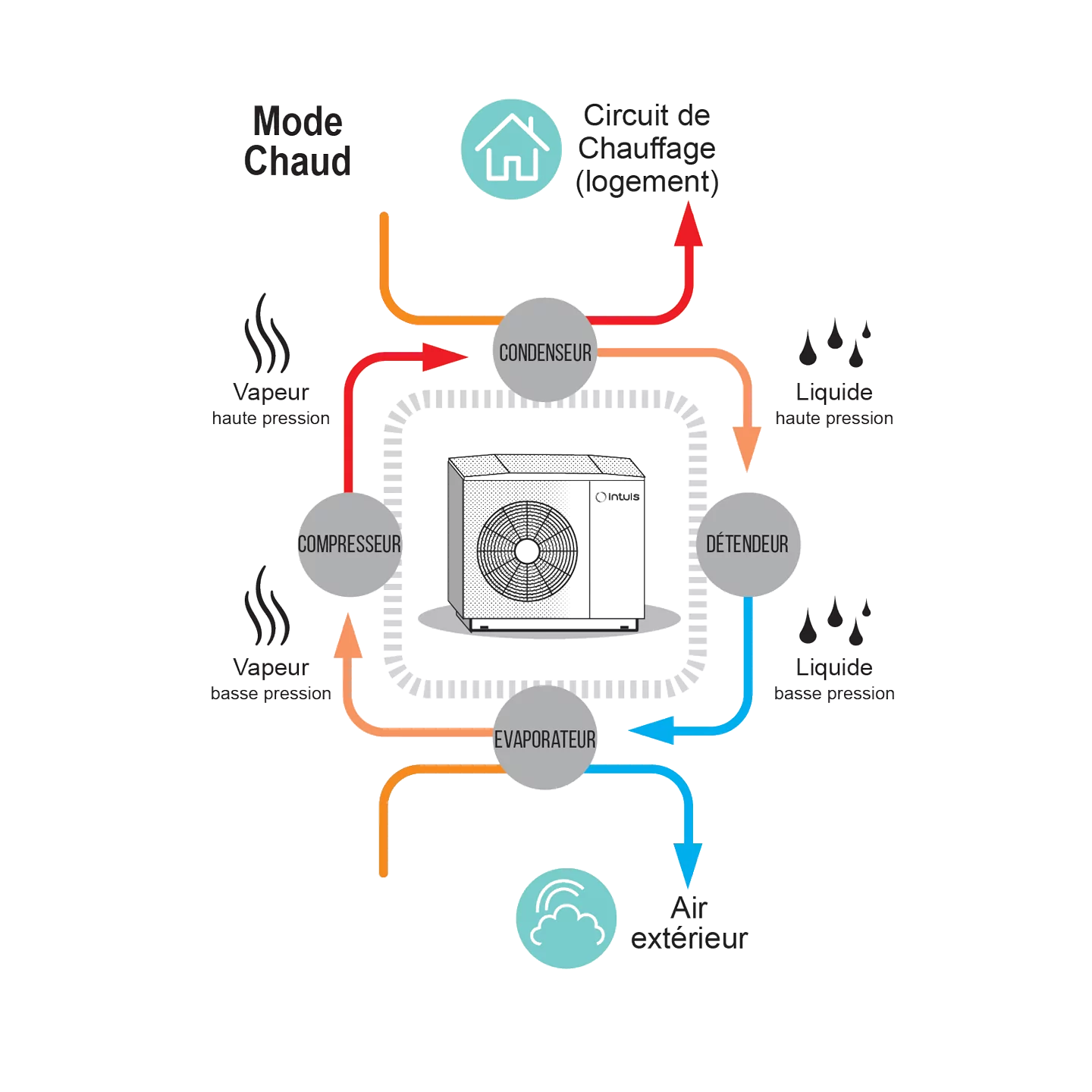
Before delving into the specifics of various heat pump types, it's crucial to grasp the fundamental operation of these systems. A heat pump is a heating system that employs the principles of thermodynamics to transfer heat from one location to another.
For a more in-depth understanding of its operation, please refer to the article "What Is a Heat Pump?"
Aerothermal Heat Pumps
The aerothermal heat pump is one of the most common and accessible types available on the market. It utilizes the air as an energy source to produce heat.
There are two main subtypes of aerothermal heat pumps: air-to-air heat pumps and air-to-water heat pumps.
Air-to-Air Heat Pump: The air-to-air heat pump captures heat from the outdoor air and distributes it inside your dwelling through a ventilation system. It is typically used for heating living spaces and often serves as an air conditioner.
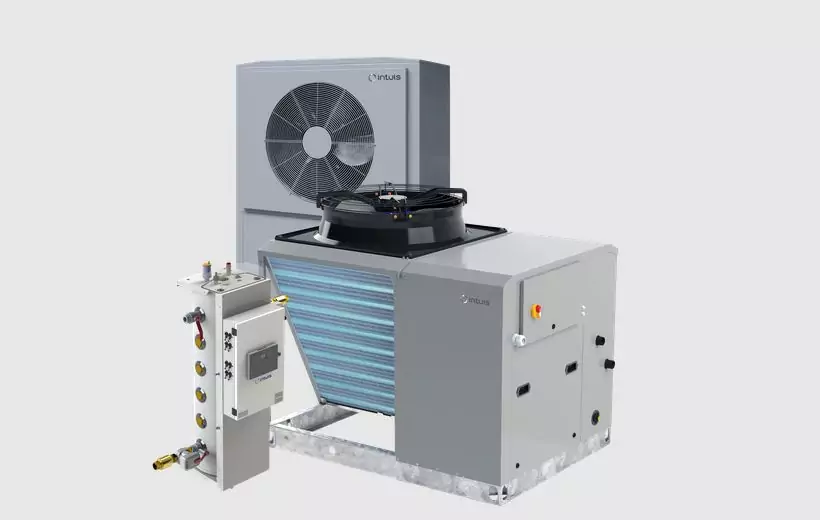
Air-to-Water Heat Pump: The air-to-water heat pump, on the other hand, harnesses the heat from outdoor air to warm water, which can then be used for heating radiators, underfloor heating, or the production of domestic hot water. Explore the range of air-to-water heat pumps by intuis.
Discover the range of intuis air-to-water heat pumps.
Hydrothermal Heat Pumps
The hydrothermal heat pump harnesses the heat contained in water, whether it's drawn from an aquifer, a lake, or a waterway. It delivers high and consistent performance throughout the year. However, its installation is more complex and requires access to a suitable water source near your residence.
You can install heat pumps in a water loop or on a district heating network. This allows for the installation of water-to-air or water-to-water heat pumps on a water loop. The idea is to utilize a loop for extracting, storing, and releasing heat. The heat is then distributed through fan coil units, ducted plenums, or floor/ceiling systems, for example.
Water Loop Heat Pumps
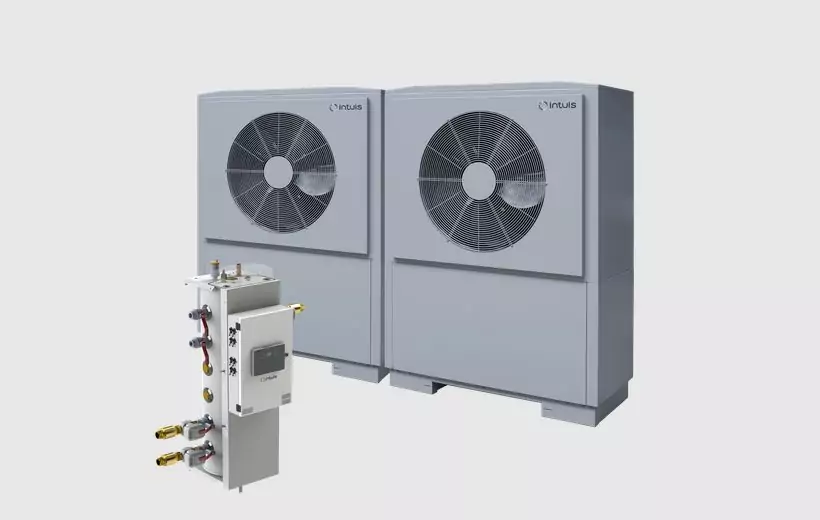
These solutions are less common but even more efficient. Heat pumps can be installed on a water loop or a district heating network. The concept is to take advantage of a loop for heat extraction, storage, and release. The heat is then distributed through fan coil units, ducted plenums, or floor/ceiling systems, for instance. These solutions are mainly used in the large tertiary sector or eco-districts. Explore intuis solutions.
Geothermal Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps utilize the heat stored in the ground to heat your residence. They require the installation of a geothermal loop, which can be either horizontal (buried at shallow depths) or vertical (deep boreholes). This system is efficient and long-lasting, providing high performance throughout the year. However, it may entail significant work for installation and the need for a construction permit.
What Type of Heat Pump to Choose?
The choice of heat pump type depends on several factors, including the characteristics of your residence, your geographical location, your heating requirements, and, of course, your budget.
Choosing the Right Heat Pump for Your Home
The air-to-water heat pump provides an efficient and comfortable heating solution for living spaces and can also produce hot water. It's an ideal replacement for a boiler. However, for those on smaller budgets, air-to-air heat pumps can be installed, though they offer less comfort. Air-to-air heat pumps are less comfortable because they deliver hot air through forced airflow rather than gradual diffusion. They are also less environmentally friendly as they tend to be more polluting.
If you have access to a nearby water source, the hydrothermal heat pump can be an excellent option. It offers consistent performance throughout the year and is less dependent on climate variations. However, its installation can be more complex and requires a higher initial investment.
Lastly, if you're looking for a sustainable and highly energy-efficient heating solution, consider the geothermal heat pump. Although it requires a more complex installation and a larger upfront investment, it delivers high performance and greater energy self-sufficiency. It is particularly well-suited for regions with colder winter temperatures.
There are also increasing numbers of eco-districts with water loop systems, which are highly beneficial for heating and cooling applications.

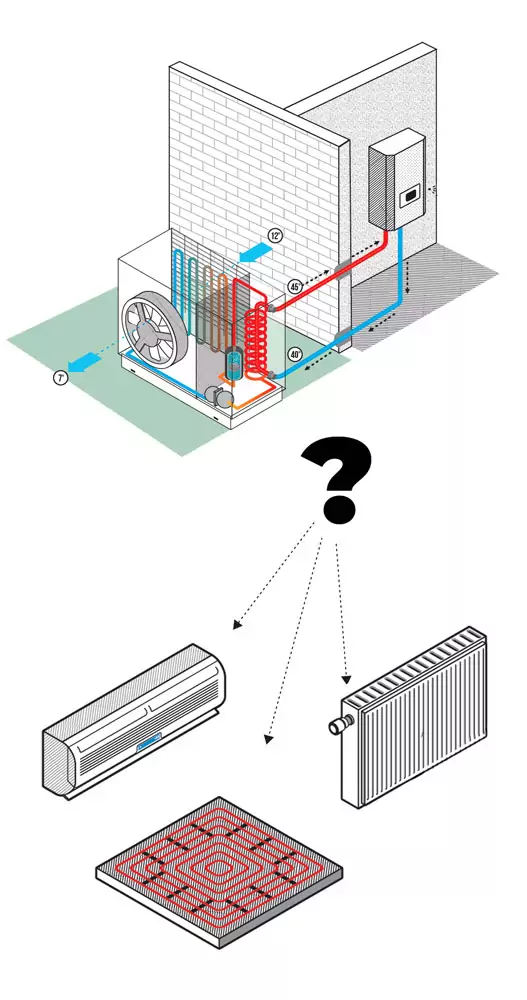
With a Heat Pump: Radiators or Underfloor Heating?
There are different types of heat emitters:
- High-temperature radiators (>65°C) typically used with gas and oil boilers.
- Medium-temperature radiators (55-65°C).
- Low-temperature radiators (50-55°C).
- Fan coil units (45-50°C).
- Underfloor/Ceiling heating (30-35°C).
These emitters operate at different water temperature ranges. The lower the temperature at which the heat generator operates, the better its efficiency. Emitters that function at lower temperatures generally provide higher comfort levels. However, it's worth noting that the air distribution with fan coil units may be less comfortable as air is blown or forced out.
A heat pump that can produce high-temperature output can also provide medium or low-temperature heat. The reverse is not true. The more versatile a heat pump is in delivering high-temperature output, the better it performs at lower temperature settings.
The advantage of a high-temperature heat pump is that it can be installed in older systems as a direct replacement for the existing heat generator. However, it is recommended to improve insulation and prioritize low-temperature emitters to enhance comfort and thermal performance.
Which is the most economical heat pump?
Economically, each type of heat pump has its own advantages. Aerothermal heat pumps are generally more affordable in terms of installation costs, but their efficiency can vary depending on climatic conditions. Geothermal heat pumps, although more expensive to install, offer high energy efficiency and long-term savings.
It's also important to consider the quality and reliability of different heat pump brands on the market. Conduct thorough research, read user reviews, and consult professionals for recommendations on reputable brands that offer reliable and durable performance.





